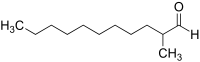
2-Methylundecanal
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Methylundecanal[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
| 110-41-8 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 54990 5291693 (2R)-2-methyl 553128 (2S)-2-methyl |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.424 |
| EC Number | 203-765-0 |
| PubChem | 61031 6915922 (2R)-2-methyl 637522 (2S)-2-methyl |
| RTECS number | YQ1509000 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H24O | |
| Molar mass | 184.32 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Density | 830.3 mg cm−3 |
| Boiling point | 171 °C; 340 °F; 444 K |
| Refractive index (nD) |
1.432 |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases | R52, R53, R38 |
| Flash point | 93.4 °C (200.1 °F; 366.5 K) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related alkyl aldehydes |
Hexyl cinnamaldehyde |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
2-Methylundecanal is an organic compound that is found naturally in kumquat peel oil.[2] This compound smells herbaceous, orange, and ambergris-like.[3] At high dilution it has a flavor similar to honey and nuts.[2] It is a colorless or pale yellow liquid that is soluble in organic solvents such as ether and ethanol.[4] It is used as a fragrance component in soaps, detergents, and perfumes.
Preparation
The first synthesis of 2-methylundecanal was recorded by Georges Darzens in 1904 from methyl nonyl ketone and ethyl chloroacetate.[5] This method of synthesis can be used to produce a variety of aldehydes and became known as the Darzens reaction and is still used today. 2-Methylundecanal is synthesized in industry by two main routes. The first route, like Darzens, involves converting methyl nonyl ketone to its glycidate by allowing it to react with alkyl chloroacetate. The glycidate then undergoes saponification followed by decarboxylation.[6]
- CH3(CH2)8C(O)CH3 + ClCH2CO2CH3 → CH3(CH2)8CH(CH3)OCH(CO2R) + HCl
- CH3(CH2)8CCH3OCCO2CH3 + H2O → CH3(CH2)8CH(CH3)CHO + CO2 + ROH
The second method for the synthesis of 2-methylundecanal begins with the conversion of undecanal to 2-methyleneundecanal by allowing it to react with formaldehyde in the presence of base. The 2-methyleneundecanal is then hydrogenated to give 2-methylundecanal. The required undecanal is generated from 1-decene by hydroformylation. The resulting solution is over 50% 2-methyleneundecanal. The double bond of this compound is hydrogenated and the resulting 2-methylundecanal is separated from the by-products using fractional distillation.[6]
- CH3(CH2)7CH2=CH2 + H2 + CO → CH3(CH2)10CHO
- CH3(CH2)10CHO + HCHO → CH3(CH2)8C(CH2)CHO + H2O
- CH3(CH2)8C(CH2)CHO + H2 → CH3(CH2)8CH(CH3)CHO
Chirality
2-Methylundecanal contains one asymmetric carbon atom.

The enantiomers can be synthesized with high enantiomeric purity using the SAMP/RAMP hydrazone method. This process involves starting with simple achiral aldehydes and converting them to their SAMP hydrazones then obtaining the corresponding chiral hydrazones using RAMP as a chiral auxiliary. The chiral hydrazones are then metalated with lithium diisopropylamide (LDA) and alkylated with a slight excess of dimethyl sulfate. Testing of the enantiomers by a professional perfumer indicated only a slight difference in odor quality and intensity.[7]
Applications
2-Methylundecanal is used widely as a fragrance element in soaps and detergents as well as in the perfume industry to give conifer notes, fir in particular, but is also used in fantasy compositions.[6] This aldehyde was one of the first synthetics to be used in a prestigious perfume, namely Chanel No. 5.[8]
References
- ↑ "2-Methylundecanal - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 26 March 2005. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 12 October 2011.
- 1 2 Fenorali, Giovanni (2004). Fenorali’s Handbook of Flavor Ingredients (5th ed.). Boca Raton: CRC Press.
- ↑ Molecule of the Month: Chanel No 5 and 2-methylundecanal
- ↑ CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (89th ed.). CRC Press. 2008–2009.
- ↑ Darzens, Georges (1904). Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires des seances de l'Academie des Sciences.
- 1 2 3 Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry (7th ed.). Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons Inc. 2009.
- ↑ Dyker, Hubert (1990). Synthesis and Properties of Enantiomers of the Two Artificial Fragrances Lilial and Methylundecanal.
- ↑ Ramsden, E.N. (2000). A-Level Chemistry (4th ed.). UK: Nelson Thornes.
External links
Further reading
- Burdock, George A., Fenorali, Giovanni. Fenorali’s Handbook of Flavor Ingredients, 5th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, 2004. ISBN 0-8493-3034-3
- Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 7th Ed: Fragrances and Flavors, John Wiley & Sons Inc, Hoboken 2009. doi:10.1002/14356007.a11_141
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. 89th ed. [Online] 2008-2009.
- Darzens, Georges; Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires des séances de l’Academie des Sciences. 1904, 139, 1214-1217.
- Dieter Enders; Hubert Dyker, Synthesis and Properties of Enantiomers of the Two Artificial Fragrances Lilial and Methylundecanal. Institut für Organische Chemie der Rheinisch-Westfälischen Technischen Hochschule. 1990, 1107–1110, http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/journal/112355592/abstract?CRETRY=1&SRETRY=0. doi:10.1002/jlac.1990199001200.
- Ramsden, E. N. A-Level Chemistry. 4th ed. Nelson Thornes: UK, 2000.